Caganon, Kurt Emmanuel P.
Grade 11 | Block 2 - Berners
Assignment in ICT Programming
The Relational Operators
| Symbol | Name |
|---|---|
| == | Equal To |
| != | Not Equal To |
| > | Greater Than |
| < | Less Than |
| >= | Greater Than Or Equal To |
| <= | Less Than Or Equal To |
Examples Of Usage
Example 1:
public static main(String[] args){
int x=10, y=10;
if (x==y){
System.out.println("X is equals to Y.");
} else {
System.out.println("X is not equals to Y.");
}
return 0;
}Output:
X is equals to Y. Here, we have used the 'Equal To' operator (==) in our if-statement's condition. When used, code below the if-statement will be invoked only if the two items between our relational operator is equal in value.
Since both x and y -- our two items are equal, the code contained by the if-statement will be executed. The code in the else-statement is ignored as the if-statement's condition was met.
The condition can be read as "If x is equal to y."
Example 2:
public static main(String[] args){
if (0!=1){
System.out.println("Zero is not equal to 1.");
} else {
System.out.println("The threads of reality are ripping apart!");
}
return 0;
}Output:
Zero is not equal to 1. Now, we have used the 'Not Equal To' operator (!=) which meets its condition if the two items between it are not equal in value.
Again, the else-statement is ignored, as the main condition is met: 0 is not equal to 1.
Example 3:
public static main(String[] args){
int c = 0;
while (c<5){
System.out.println(c);
c=c+1;
}
System.out.println("Done!");
return 0;
}Output:
0
1
2
3
4
Done! Lastly, we have used the 'Lesser Than' operator (<) in what's called a 'while-loop'. The while-loop executes the code it contains if its condition is met, then repeats until the condition is no longer true.
In the example, we made a variable c, which increases by 1 every time the code in the while-loop is iterated, until it reaches a value of 5, because 5 is not at all lesser than itself. We can read the condition as "Repeat while c is less than 5".
Syntax Of Relational Operations
item1 operator item2
where item1 and item2 is a value (variable, constant, or function return value)
and operator is a relational operator.
Examples:
foo == fey
input != BADWORD
numCounter < 25
The Decision Symbol and Branch Flowcharts.

The Decision Symbol - a diamond.
The decision symbol is used to ask a question or create conditions. The answers or the outcomes are determined by the two flow lines that branch off of it.
The flow lines that comes after this symbol should be labeled as 'Yes' and 'No' or 'True' and 'False', and they correspond to the two outcomes when the condition described in the decision symbol is met or unmet.
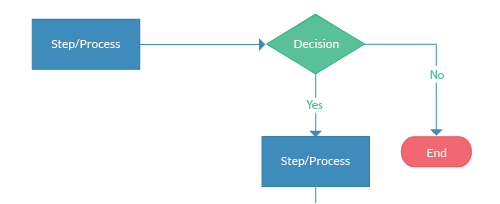
An example of Decision Symbol usage.
The appearance of the Decision Symbol will always result in a branched flow of logic. Flowcharts with a branched flow of logic are called Branch Flowchart, and will always utilize one or more Decision Symbols.
This is in contrast to a Sequence Flowchart, where the flow of logic is only linear, and will never branch at all (as there is a lack of the Decision Symbol in its flow of logic).
Sources:
(Ultimate Flowchart Tutorial) Nishadha, via creately.com/blog/diagrams/flowchart-guide-flowchart-tutorial/
(Decision Symbol Usage Image) Nishadha, via creately.com/blog/diagrams/flowchart-guide-flowchart-tutorial/
(Flowchart_Decision.svg) DevinCook, CC BY-SA 4.0 https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0, via Wikimedia Commons
Example Of A Branch Flowchart
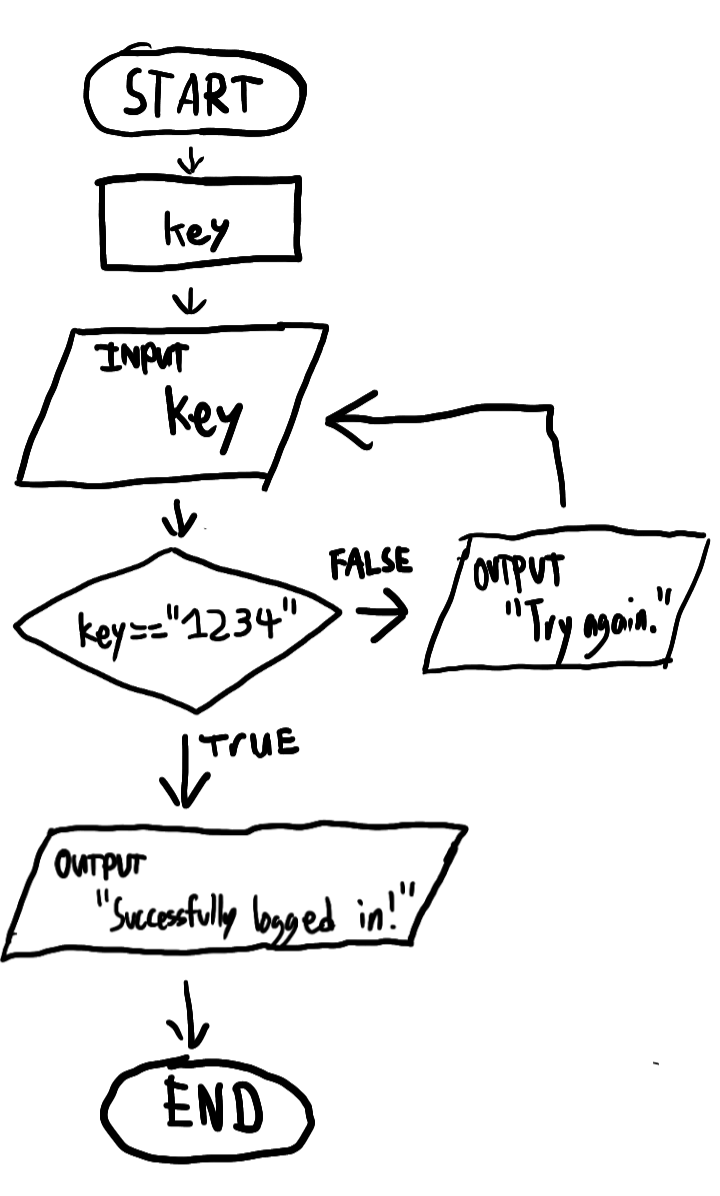
This flowchart depicts a system where a user has to enter a programmer-defined password. I will dictate the flow of logic by word:
First we declare a variable key.
We then ask for user input, storing it unto the key variable.
After that, we encounter a condition.
If the key variable is equal to "1234", the condition is true and we then proceed onto:
Displaying
"Successfully logged in!"Ending the flow of logic
Else, if the condition is unmet, we then proceed onto:
Displaying
"Try again."Jumping back onto the previous input query for
keyfor the user to enter another passwordRepeating the condition check.
The flow of logic only ends with the user providing a correct password.